* Only visible on admin mode.
Data Layer Value
Value
DataLayer - GTM_Page_Type
DataLayer - GTM_page_category
Front Row MD ID

Content
Author
Date
Category
Tags
Know Your Oats: A Comprehensive Guide
Immunity, Lifestyle, Longevity

Author
Shana Reed
January 16, 2025
Shana Reed
Introduction
Introduction
Oats are much more than a breakfast staple.
They’re a superfood with an impressive nutritional profile, a wide range of health benefits, and incredible versatility in cooking.
Whether you are trying to lose weight, support heart health, or enjoy a wholesome meal, oats deserve a prominent spot in your kitchen.
This guide explores the fascinating history, health benefits, and practical uses of oats and insights into how they can transform your diet and well-being.
1. The History of Oats
1. The History of Oats

Origins and Early Cultivation
Origins and Early Cultivation
Oats (Avena sativa) originated in the Fertile Crescent, thriving as wild grains alongside early agricultural staples like wheat and barley.
Unlike their counterparts, oats were initially considered weeds due to their lower yields and complex processing.
However, by 1000 BCE, their adaptability to cooler, wetter climates made them indispensable, particularly in Northern Europe.
Transition to Human Consumption
Transition to Human Consumption
Initially used as animal fodder, oats gradually transitioned into human diets during food scarcity.
By the Middle Ages, they became a staple in Scotland and Scandinavia, regions less suited to wheat cultivation.
The Scots, in particular, embraced oats as a dietary cornerstone, featuring them in iconic dishes like porridge and haggis.
2. Types of Oats
2. Types of Oats
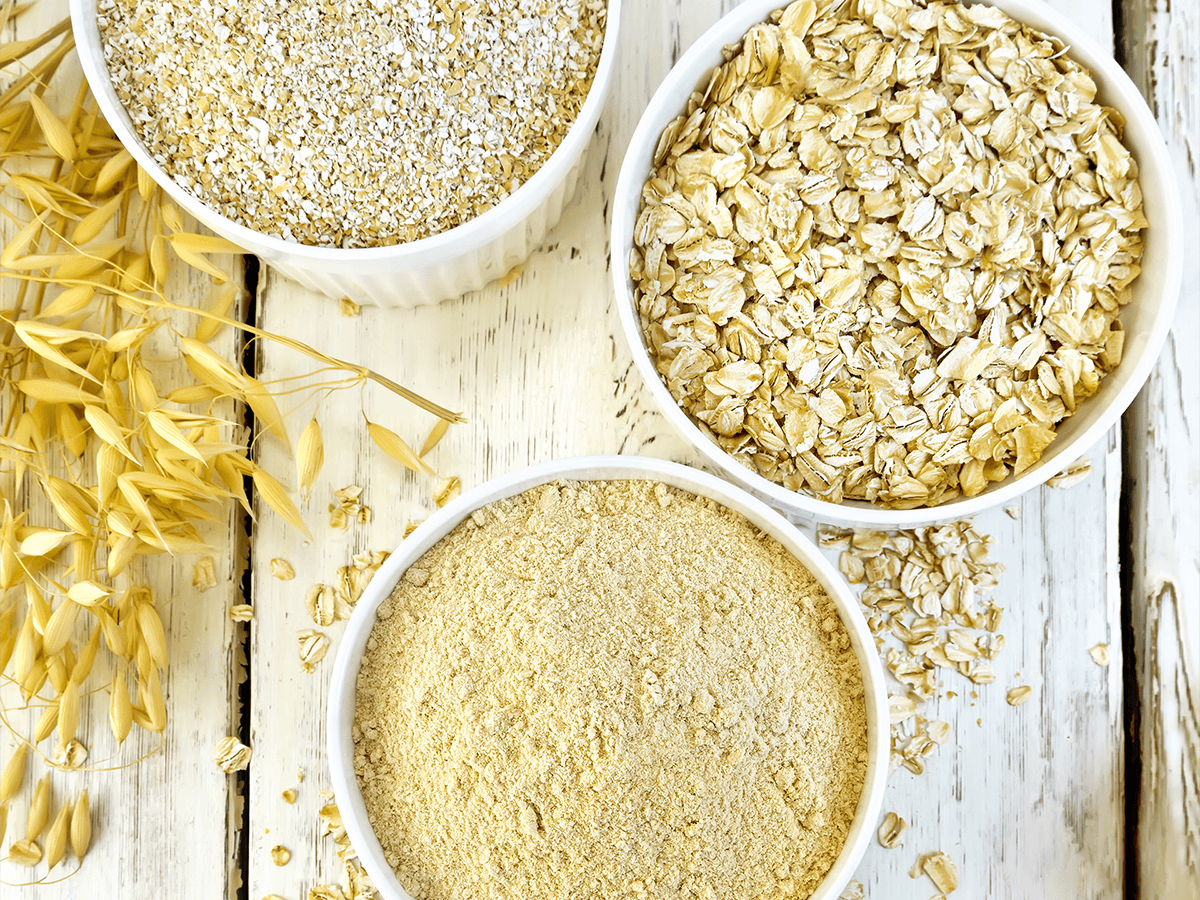

Understanding the types of oats can help you choose the right one for your health goals and culinary preferences.
- Whole Oat Groats: The least processed form, retaining a chewy texture and robust flavor. It is ideal for salads, soups, and hearty grain bowls.
- Steel-Cut Oats: Nutty and firm, they are perfect for a wholesome breakfast. They take longer to cook but provide sustained energy.
- Rolled Oats: Steamed and flattened, these versatile oats are great for oatmeal, granola, and baking.
- Quick Oats: Thinner than rolled oats, they cook in minutes, making them ideal for busy mornings.
- Instant Oats: Pre-cooked and dried for near-instant preparation, though often less textured and nutritious.
- Oat Bran and Oat Flour: High-fiber oat bran and gluten-free oat flour are excellent for baking and dietary supplementation.
3. Nutritional Profile of Oats
3. Nutritional Profile of Oats

Oats are a nutritional powerhouse packed with essential macronutrients, micronutrients, and fiber.
Macronutrients
Macronutrients
Oats are rich in complex carbohydrates, providing sustained energy without blood sugar spikes. They also contain 10-17% protein, more than most other grains, making them ideal for active lifestyles.
Micronutrients
Micronutrients
Key vitamins and minerals include magnesium, iron, zinc, and B. These support everything from energy production to immune health and bone strength.
Fiber
Fiber
The high fiber content, particularly beta-glucan, is a standout feature of oats.
This soluble fiber is linked to lower cholesterol levels, improved gut health, and better blood sugar control.
4. Oats for Weight Loss and Management
4. Oats for Weight Loss and Management
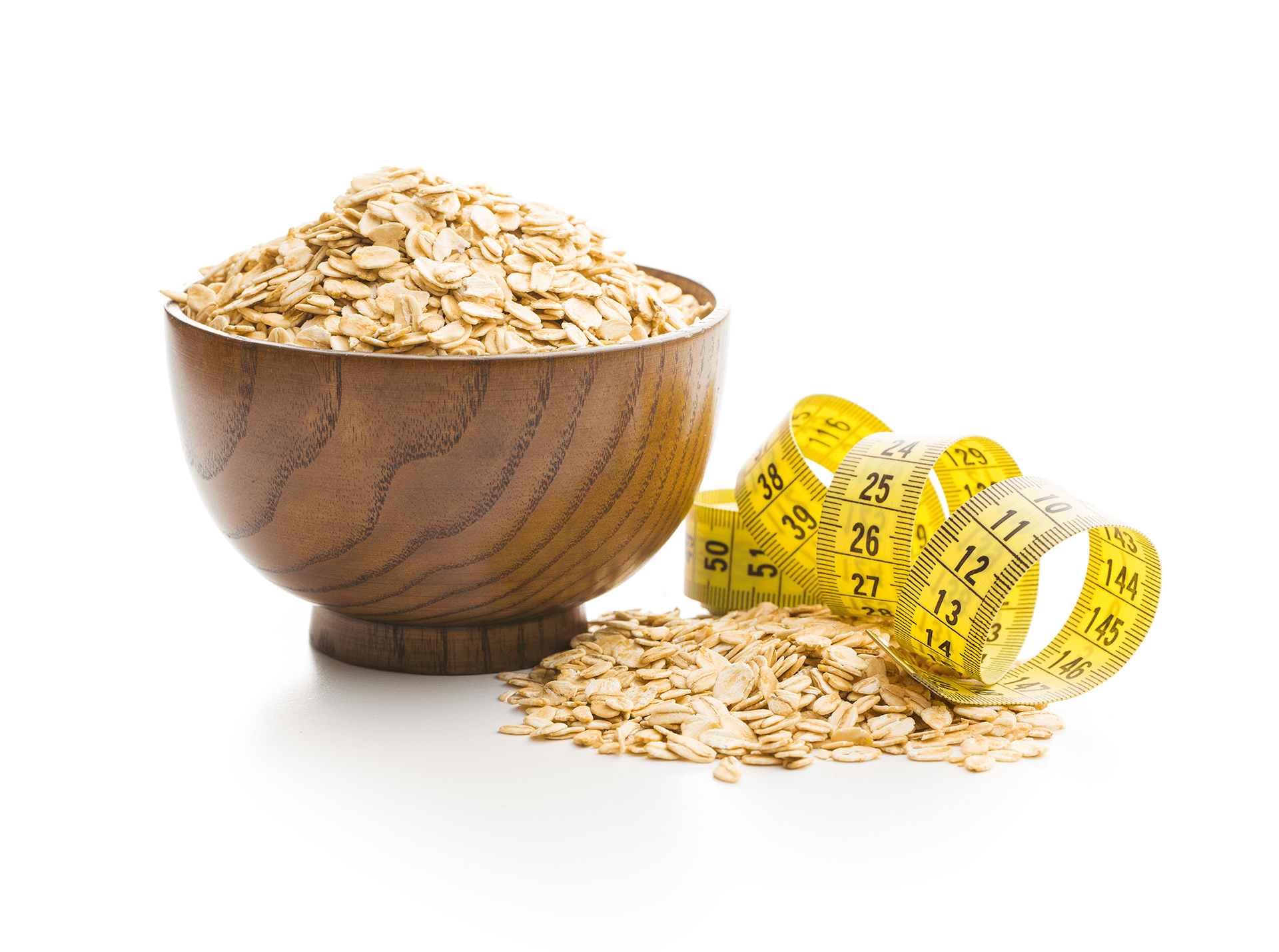

How Oats Promote Weight Loss
How Oats Promote Weight Loss
Oats are a natural appetite suppressant. Their high fiber content increases satiety by slowing digestion and stabilizing blood sugar levels.
Beta-glucan’s ability to form a gel-like substance in the gut enhances the release of satiety hormones, helping control cravings.
Glycemic Control and Energy Balance
Glycemic Control and Energy Balance
Oats have a low glycemic index (GI), releasing glucose slowly into the bloodstream.
This prevents energy crashes, reduces hunger, and supports consistent calorie intake, all critical for weight management.
Practical Meal Ideas
Practical Meal Ideas
- Breakfast: For a protein-packed start, combine steel-cut oats with fresh berries, chia seeds, and a dollop of Greek yogurt.
- Lunch: Use rolled oats as a base for a savory grain bowl topped with roasted vegetables and grilled chicken.
- Snacks: Make oat-based energy bars with nuts, honey, and dark chocolate for a nutritious pick-me-up.
5. Oats for Heart Health
5. Oats for Heart Health
The Science Behind Oats and Heart Health
The Science Behind Oats and Heart Health
Oats are endorsed by health organizations worldwide for their cardiovascular benefits.
Studies show that consuming 3 grams of beta-glucan daily (equivalent to 1½ cups of cooked oats) can significantly lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol by binding to bile acids and removing them from the body.
Heart-Healthy Recipes
Heart-Healthy Recipes
- Oatmeal with Almonds and Blueberries: Add antioxidant-rich toppings for a double boost to heart health.
- Oat-Crusted Fish: Use oats as a crunchy coating for baked salmon or cod.
- Savory Oat Risotto: Replace rice with steel-cut oats for a heart-healthy twist on a classic dish.
6. Oats for Digestive and Gut Health
6. Oats for Digestive and Gut Health

Prebiotic Properties
Prebiotic Properties
Oats act as a prebiotic, feeding beneficial gut bacteria and promoting a balanced microbiome. A healthy gut improves immunity, digestion, and mental well-being.
Relieving Digestive Issues
Relieving Digestive Issues
Combining soluble and insoluble fiber in oats supports smooth digestion and prevents constipation. For those new to high-fiber diets, gradually increasing oat consumption can prevent bloating.
7. Versatile Uses of Oats
7. Versatile Uses of Oats
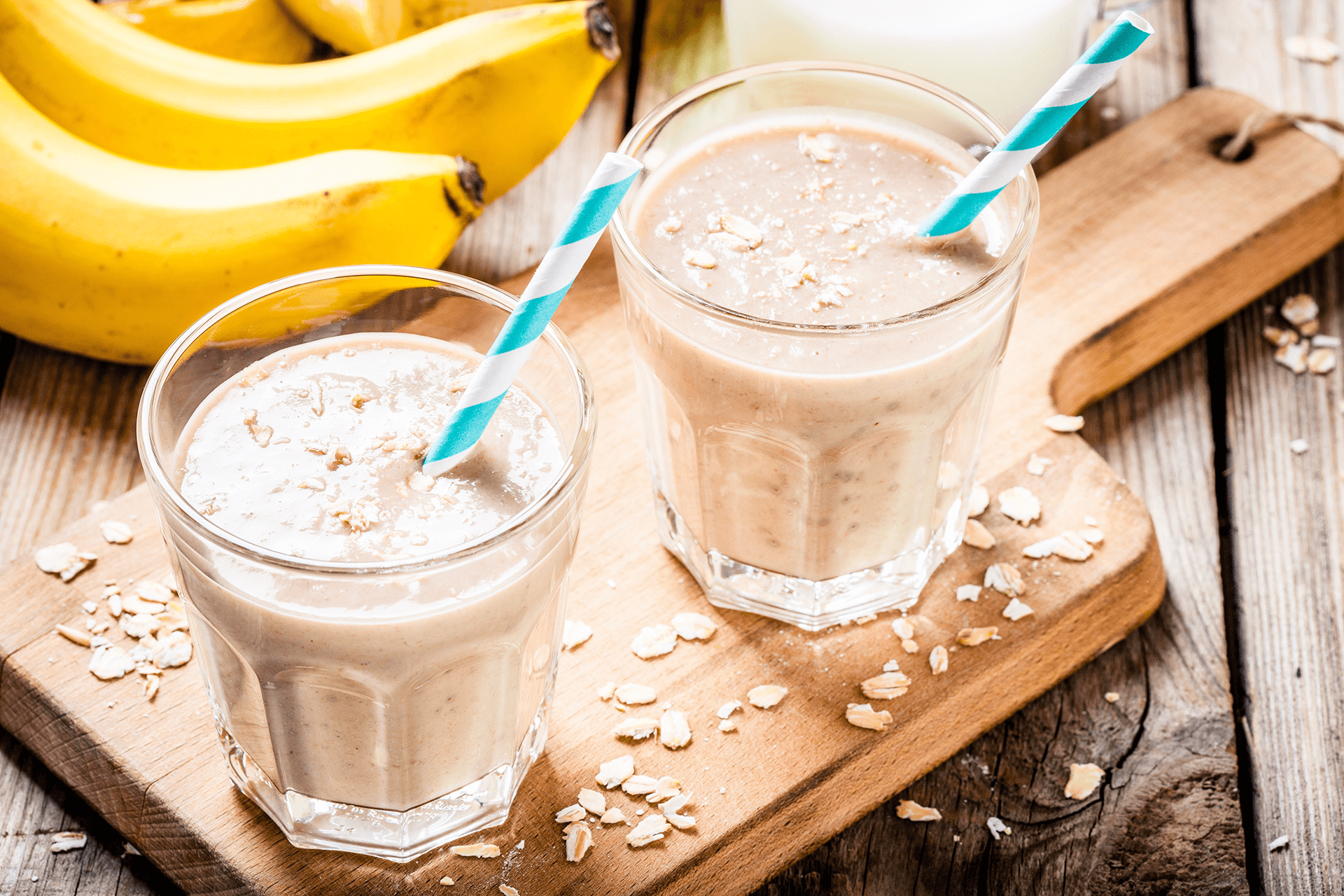

Beyond the Bowl
Beyond the Bowl
- Baking: Incorporate oats into muffins, cookies, and granola bars.
- Smoothies: Add a handful of oats for extra fiber and creaminess.
- Skincare: Use finely ground oats as a natural exfoliant or soothing face mask.
For Athletes
For Athletes
Oats provide sustained energy, making them a go-to choice for pre-and post-workout meals.
Combine them with bananas and peanut butter for a quick energy boost.
FAQs About Oats
FAQs About Oats
Can oats help with cholesterol management?
Can oats help with cholesterol management?
Yes, beta-glucan in oats lowers LDL cholesterol, reducing the risk of heart disease.
Are oats gluten-free?
Are oats gluten-free?
Pure oats are naturally gluten-free, but cross-contamination can occur. Look for certified gluten-free oats if you have celiac disease.
How do oats aid in weight loss?
How do oats aid in weight loss?
Oats increase satiety, regulate blood sugar, and prevent cravings, supporting calorie control.
What’s the best way to store oats?
What’s the best way to store oats?
Store oats in an airtight container in a cool, dry place. For extended freshness, refrigerate or freeze them.
Can oats be eaten raw?
Can oats be eaten raw?
Yes, but soaking improves digestibility and nutrient absorption.
Are flavored instant oats healthy?
Are flavored instant oats healthy?
Flavored oats often contain added sugars. Choose plain varieties and enhance flavor with fresh fruit or spices.
Conclusion
Conclusion
Oats are a true nutritional gem, offering many health benefits and culinary possibilities.
Whether striving for weight loss, heart health, or simply delicious meals, oats are a versatile and sustainable choice.
Make oats a regular part of your diet and enjoy the remarkable benefits they bring to your life.

Author
Shana Reed
-
Latest Posts
-
-
The Power of Fiber: Why Your Body Loves It and How to Get More
-
Know Your Oats: A Comprehensive Guide
-
5 Steps to a Healthier You
-
Advancing Health with GLP-1: Innovations, Applications, and Future Directions
-
Understanding and Managing Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Prevention, Treatment, and Complications
-
-
Contacts
Contacts
967 E. Parkcenter Blvd #345
Boise, ID 83706
7 A.M. - 3 P.M. MST, Mon - Fri
(833) 332-8655
support@clinicaleffects.com
THE STATEMENTS MADE ON OUR WEBSITES HAVE NOT BEEN EVALUATED BY THE FDA (U.S. FOOD & DRUG ADMINISTRATION). OUR PRODUCTS ARE NOT INTENDED TO DIAGNOSE, CURE OR PREVENT ANY DISEASE. CLINICAL EFFECTS IS NOT AFFILIATED WITH ANY OF THE STUDIES MENTIONED ON THE WEBSITE. THE TESTIMONIALS ON THIS WEBSITE ARE INDIVIDUAL CASES AND DO NOT GUARANTEE THAT YOU WILL GET THE SAME RESULTS.
© All Rights Reserved 2021








