* Only visible on admin mode.
Data Layer Value
Value
DataLayer - GTM_Page_Type
DataLayer - GTM_page_category

Content
Author
Date
Category
Tags
Maximize Gains with Strategic Heavy Lifts: The Ultimate Guide
Immunity, Lifestyle, Longevity
Author
Sydney E.
April 8, 2024
Sydney E.
Key Takeaways
Key Takeaways
- Heavy lifting is defined by individual one-repetition maximum (1RM), targets myofibrillar hypertrophy, and positively impacts metabolism and body composition.
- Key principles for effective heavy lifting emphasize mastering proper technique, focusing on progressive overload, and prioritizing rest and recovery to promote muscle growth and prevent injury.
- Nutrition, safe lifting practices, such as using a spotter, and strategies to overcome plateaus are essential for maximizing the benefits of heavy lifting and progressing in a fitness regimen.
Understanding Heavy Lifts
Understanding Heavy Lifts
Heavy lifting is often thrown around a lot in the fitness world, but what does it mean?
Heavy lifting is defined by an individual’s one repetition maximum (1RM), the maximum weight you can lift for one complete repetition. The intensity of the workout is high, meaning your muscles should be significantly stressed.
The weights are considered heavy when sets last two to three repetitions, are intense and challenging.
The classification of ‘heavy’ lifting varies and can range from weights that allow for just two to three repetitions to those that can be lifted for eight to twelve reps.
Heavy resistance training, which includes heavy lifting and working with heavy weights, is a crucial component of any well-rounded fitness program.
In strength training, the number of repetitions you can complete with a given weight helps determine its classification.
For instance, a weight heavy enough to allow only two to three repetitions is generally classified as ‘heavy’ lifting in maximum strength training.
On the other hand, light weights for four to six repetitions per set are typically used to gain general strength and fitness. Most consider weights that can be lifted for eight to twelve reps ‘heavy’ to increase strength and muscle size.
Advantages of Incorporating Heavy Lifts
- Targets myofibrillar hypertrophy, leading to stronger, thicker muscle fibers
- Promotes muscular strength and density
- Causes sufficient muscle damage, which is essential for subsequent muscle growth during recovery
- An increase in resting metabolism by approximately 50 calories per day
- A reduction in both visceral and subcutaneous fat
- Improved body composition by building lean muscle and reducing fat mass, ultimately leading to better body weight management.
Incorporating heavier weights and lifting weights into your workout routine can have these benefits.
Age is no barrier to the benefits of heavy lifting either.
Older adults can benefit from this type of training, experiencing improvements in bone density, muscle retention, and functional performance.
Moreover, during periods of caloric restriction, heavy lifting helps to retain lean muscle mass, which is crucial for long-term weight management without muscle loss.
Principles for Effective Heavy Lifting
- Mastering proper technique
- Focusing on progressive overload
- and prioritizing rest and recovery.
Prioritize Proper Technique
The first rule of heavy lifting is to prioritize proper technique.
Proper weight training techniques are vital to avoid sprains, strains, fractures, and other injuries that could impede training efforts.
Correct form enhances the effectiveness of the workout and prevents strains.
It’s about getting the most from your workout while reducing the risk of injury. Proper form involves moving through the full range of motion in the joints. If proper form cannot be maintained during an exercise, reducing the weight or the number of repetitions is advised.
Several exercises require specific form and technique.
For instance, when performing the overhead press, also known as the military press, you should press a barbell from shoulder level to overhead with arms fully extended, then lower it back down with control.
Similarly, deadlifts should be performed by stopping between reps to engage more muscle and eliminate momentum.
The close-grip bench press is performed with hands 6-8 inches apart, lowering the bar to around nipple level. Remember, maintaining good form is paramount, even when the going gets tough!
Progressive Overload
Another vital principle to incorporate into your heavy lifting routine is progressive overload.
Progressive overload is essential for continuously challenging the muscles to stimulate muscle growth and strength improvements over time.
Without progressive overload, muscles will adapt and cease to gain from the same resistance level.
There are several ways to incorporate progressive overload into your workouts. Some methods include:
- Increasing the weight lifted over time
- Altering the number of repetitions or sets
- Changing the exercise tempo
- Varying the types of exercises performed
- Adjusting the rest periods between sets
Rest and Recovery
Finally, we arrive at the third cornerstone of effective heavy lifting: rest and recovery. After challenging your muscles with a heavy lift session, it’s crucial to allow them time to recover by avoiding exercising the same muscle groups two days consecutively.
Light activity can mitigate delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS) and prepare muscles more quickly for the next heavy lifting session.
Nutrition also plays a crucial role in recovery. After exercising, consume protein and some carbohydrates to promote muscle recovery and glycogen replenishment.
A balanced meal following exercise should include vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Moreover, rest days or active recovery contribute to muscle repair and are crucial in overcoming performance plateaus.
Essential Heavy Lift Exercises
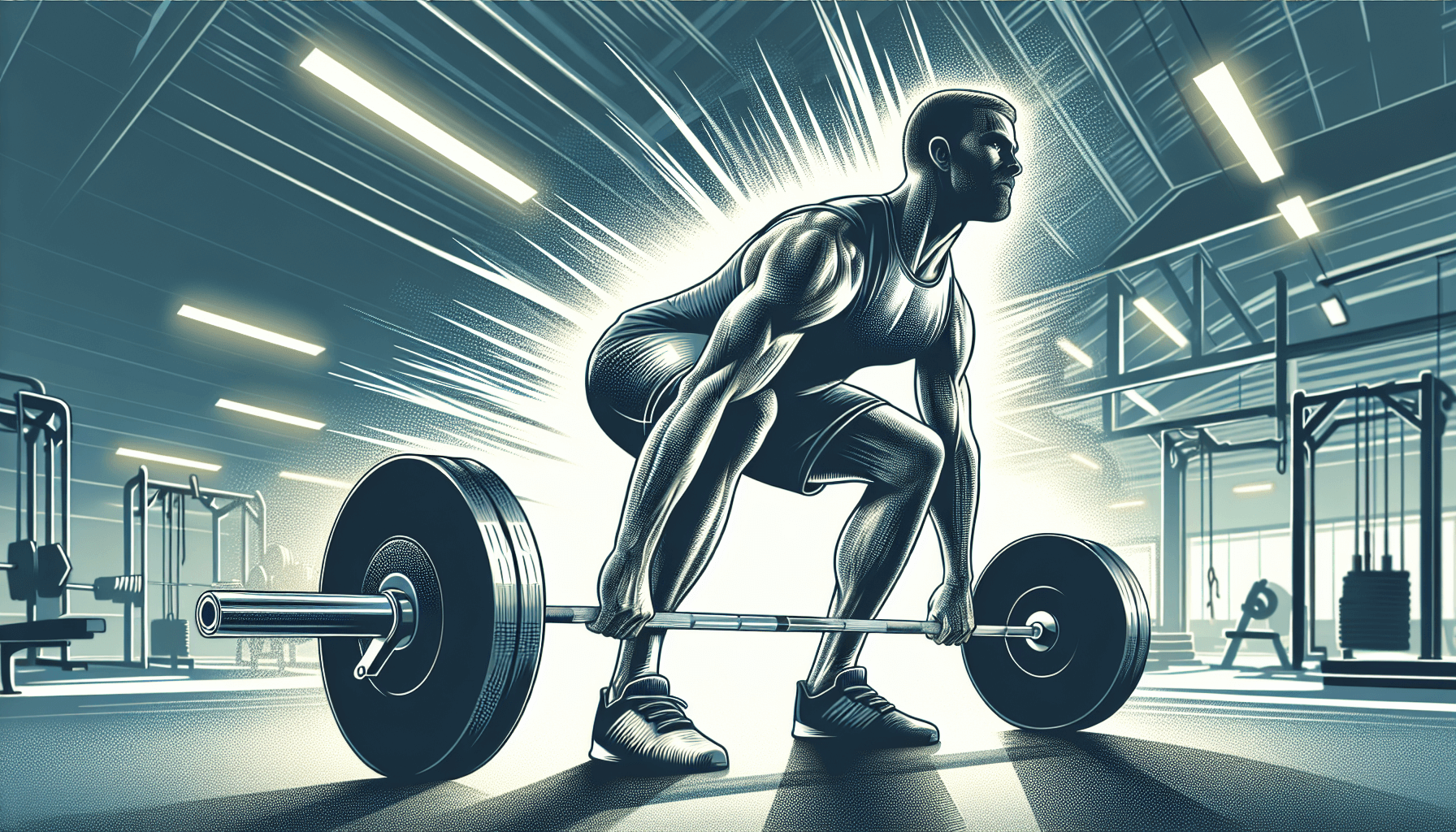
Now that we’ve covered the basic principles of heavy lifting, let’s dive into the meat of the matter—the exercises! Deadlifts, squats, and bench presses are the foundation of strength training.
Incorporating these exercises into your heavy lifting routine will set you on a solid path toward strength, muscle growth, and overall fitness.
Deadlifts
Deadlifts
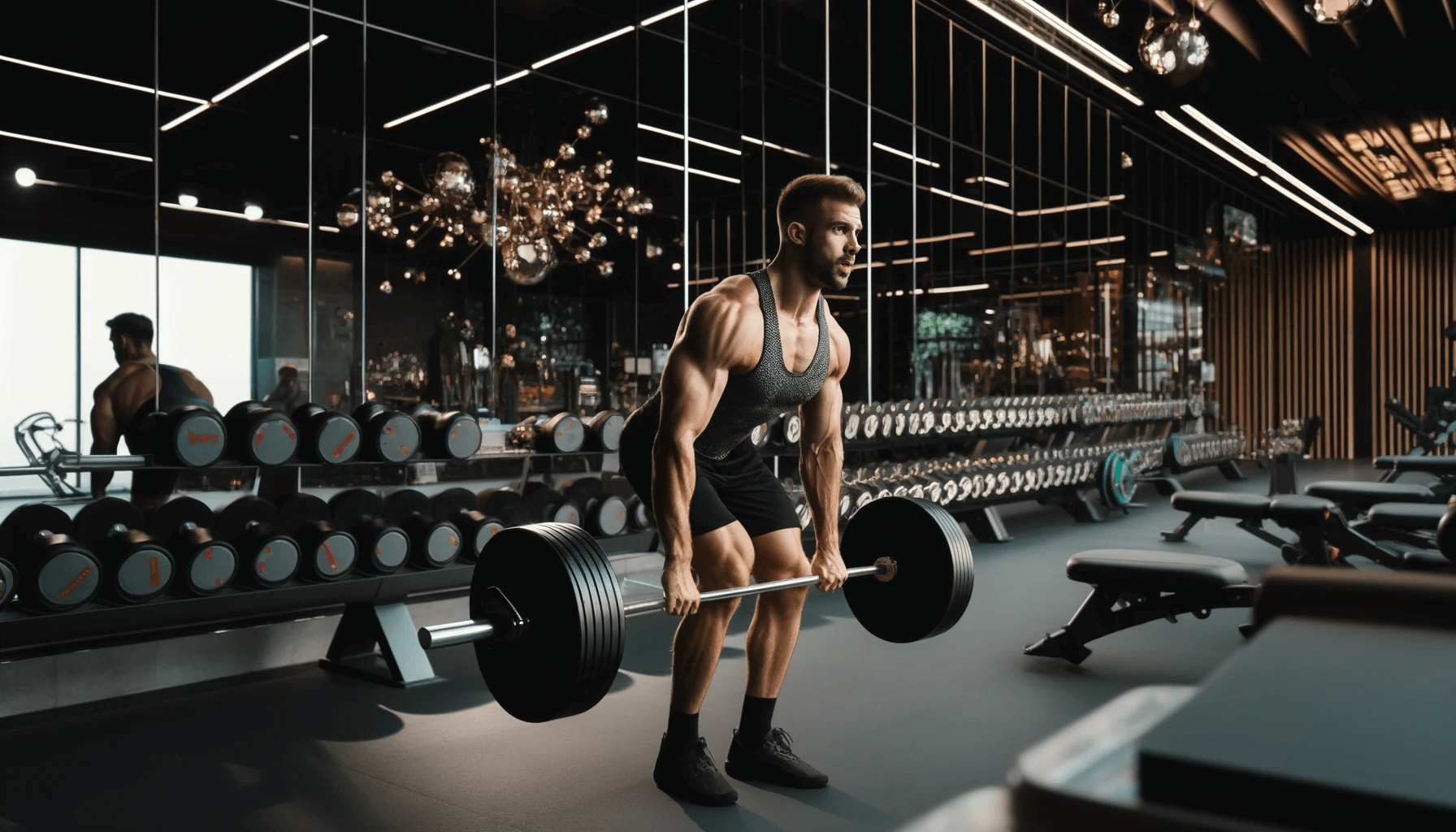

The deadlift is a powerful compound exercise that targets the major muscle groups in the lower body, including the glutes, hamstrings, and quads. The starting position for a conventional deadlift requires standing with feet about hip-width apart, toes pointing slightly outward, and gripping the barbell with hands just outside the legs.
During the lift, it is crucial to:
- Maintain a straight back
- Keep a braced core throughout the movement
- Push through the heels
- Straighten the knees and hips to raise the barbell.
Squats
Squats
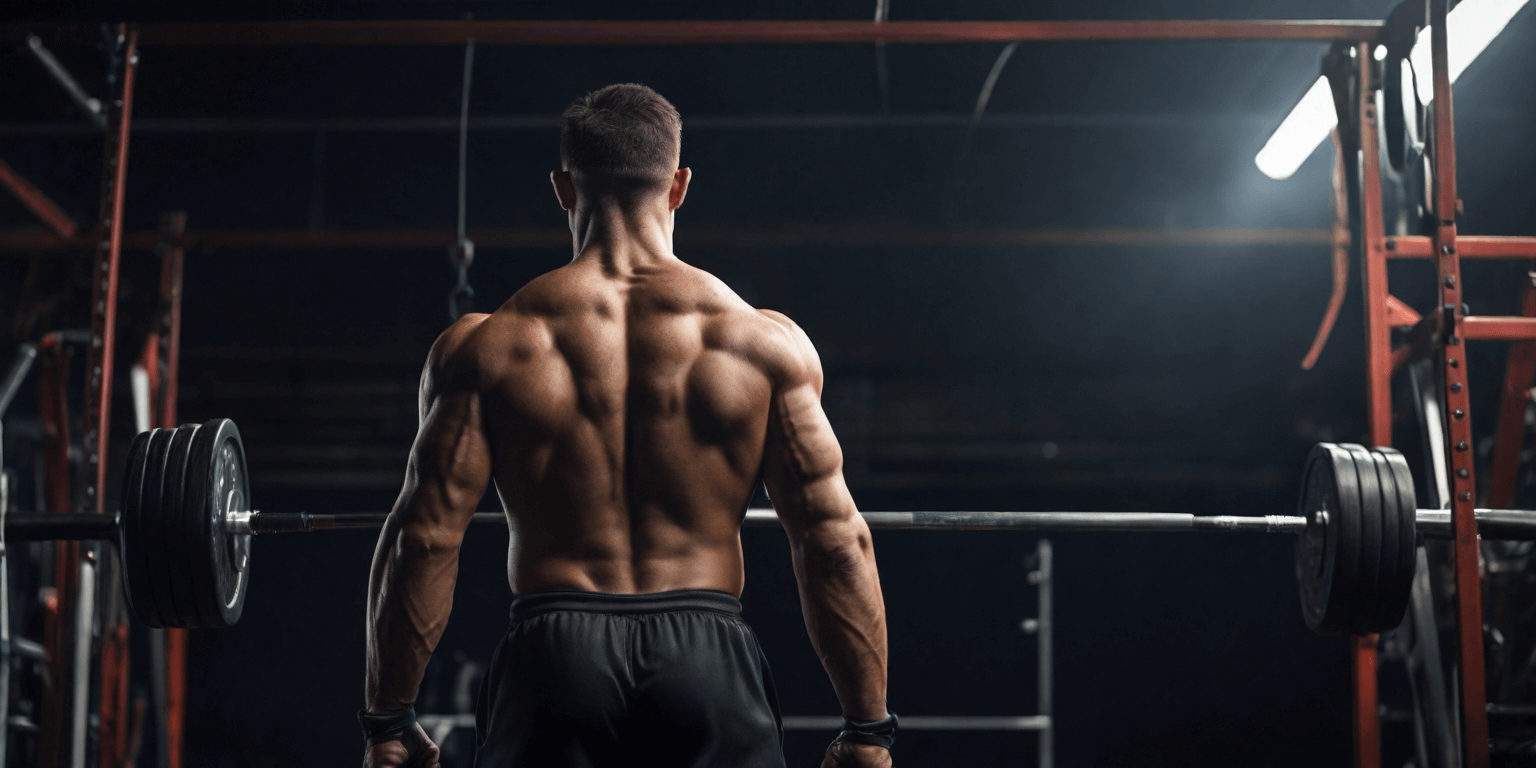

Next, we have squats - the king of all lower-body exercises. Squats engage many muscles and are valuable to any strength training routine.
The proper technique for performing squats effectively involves keeping the head upright, maintaining a slight arch in the lower back, and squatting down until the thighs are just below parallel with the ground.
There are various types of squats you can incorporate into your routine. For instance, a back squat is performed by:
- Standing under a racked barbell
- Positioning it behind the head on the traps
- Squatting straight down after tightening the abs and driving the elbows toward the floor
- Standing back up.
- Placing the barbell on the front shoulders with elbows high
- Descending by bending the knees and hips while keeping an upright torso, with knees slightly bent
- Driving up through the heels to return to a standing position.
Bench Press
Bench Press
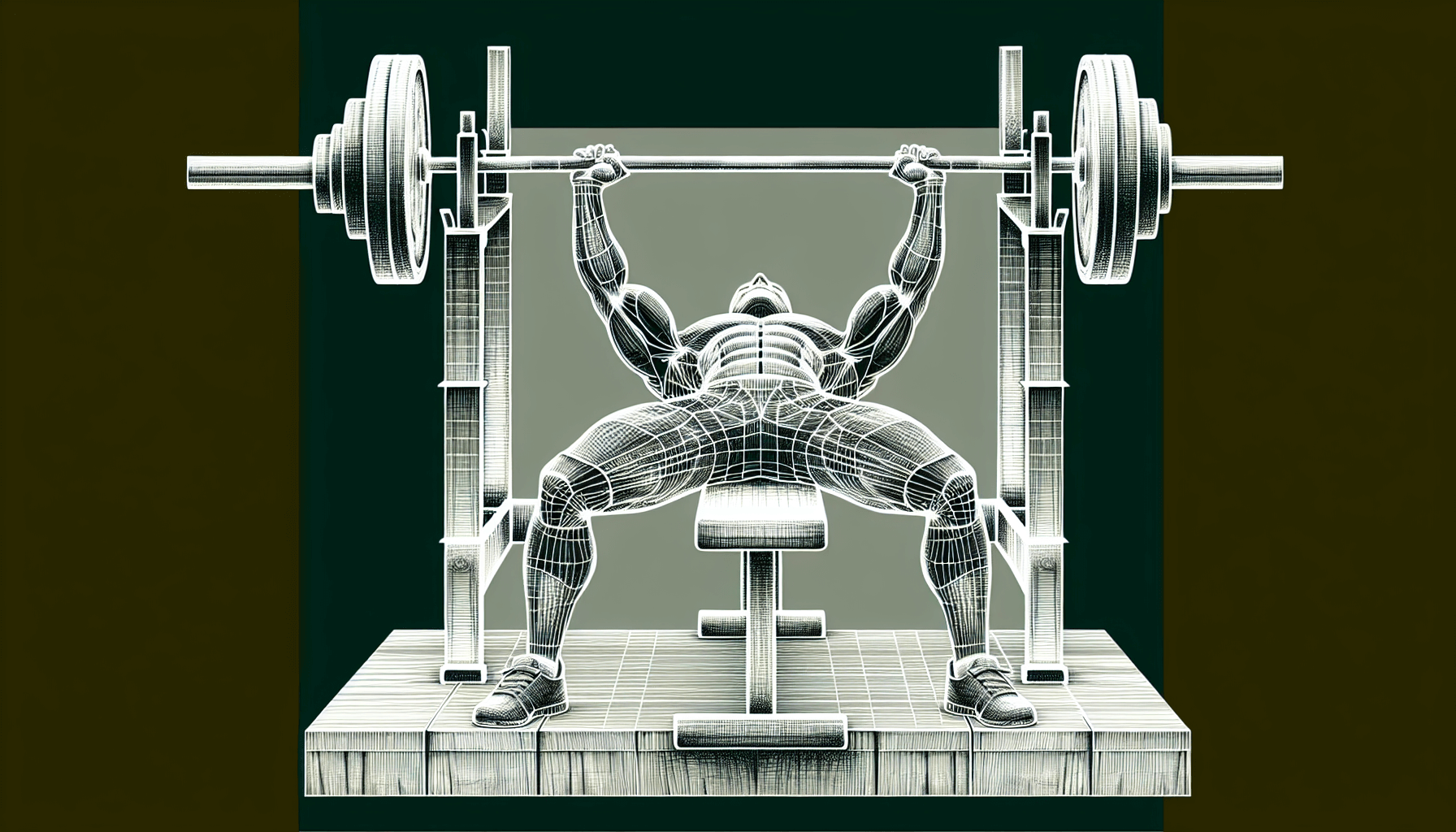
Finally, let’s discuss the bench press - a staple in any strength training program. The bench press targets the upper body, specifically the chest, shoulders, and triceps.
To perform the bench press effectively, you need to:
- Maintain a slight arch in the lower back
- Keep the back and glutes against the bench
- Pull the elbows toward the ribcage as the bar is lowered to protect the shoulders and increase the exercise’s effectiveness in building upper body strength.
Remember, mastering the bench press takes time and practice, but the results are worth the effort. So, don't shy away from the bench the next time you’re at the gym.
Instead, embrace it as a tool to build a stronger, fitter, and healthier you.
Tips for Safe and Effective Heavy Lifting

Now that we’ve covered the exercises let’s discuss some tips to ensure your heavy-lifting journey is safe and effective.
These tips, from consulting professionals to starting with moderate weights, warming up, using a spotter, and listening to your body, will help you prevent injuries and maximize gains.
Warm-Up and Stretching
Before lifting those heavy weights, it’s crucial to warm up your body.
Research indicates that warming up before a workout improves performance in most scenarios, supporting its importance for practical training.
An adequate warm-up with brisk walking or another aerobic activity reduces the risk of muscle injuries during heavy lifting.
In addition to a general warm-up, dynamic warm-up exercises like leg swings and arm circles can increase muscle elasticity and blood flow, preparing the body for weight lifting.
As part of the warm-up routine, cardiovascular activities such as jogging or jumping jacks elevate the heart rate and prepare the cardiovascular system.
Remember, starting a heavy lifting session with cold muscles increases the chance of injury, making a proper warm-up crucial.
Use a Spotter
Use a Spotter
Safety should always be a priority when lifting heavy weights. That’s where a spotter comes in. A spotter can help protect the weightlifter from dropping weights, a common cause of injury.
Not only does a spotter protect the lifter, but they also help protect the gym equipment from damage caused by weight drops or mishandling.
Furthermore, spotters ensure the safety of other gym-goers by preventing weights from accidentally injuring bystanders.
Using a spotter during heavy lifts is crucial for ensuring safety and preventing injuries. So, the next time you hit the gym, consider bringing a buddy along for those heavy lifts!
Listen to Your Body
Listen to Your Body
While striving for progress, listening to your body when heavy lifting is essential.
It is crucial to be aware of and receptive to pain, discomfort, and fatigue signals. If you experience discomfort or extreme exertion, modify or pause your workout to prevent overtraining and injuries.
Remember, exhaustion can increase the likelihood of injury by causing a lifting-form breakdown. So, listen to your body’s signals and respond appropriately. Your body knows best!
Nutrition for Heavy Lifting Success
Nutrition for Heavy Lifting Success
As we’ve learned, heavy lifting isn’t just about the weights; it’s also about what you fuel your body with.
Proper nutrition plays a pivotal role in supporting muscle development and recovery. Lean protein sources such as chicken, fish, and turkey are essential for heavy lifters.
Besides protein, you should focus on nutrient-rich foods and balance among macronutrients. Limiting sugar-laden beverages and processed foods while increasing intake of whole grains can contribute to a well-rounded diet, which is crucial for those engaged in heavy lifting.
Remember, your body is like a machine, and what you fuel it with will determine how efficiently it performs.
Overcoming Plateaus and Maximizing Progress
In your heavy-lifting journey, you may encounter plateaus - periods where progress seems to stall.
But don’t worry; these are normal and can be overcome. Introducing a combination of intensities in resistance training programs can help break through plateaus and decrease the risk of injury.
Here are some strategies to try:
- Switching up the exercises
- Trying different variations
- Increasing the weight or resistance
- Changing the number of sets and reps
- Incorporating supersets or drop sets
- Adding in new exercises or equipment
By implementing these strategies, you can provide a fresh challenge to your muscles and aid in breaking through a plateau.
Increasing training volume can help break through lifting plateaus. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Add more sets and reps to your workouts
- Include additional exercises that target different muscle groups
- Shorten rest intervals between sets to increase the intensity
- Use weights that make performing five repetitions very challenging
- Consider changing your program every 10-12 weeks to encourage continuous progress
Summary
We’ve covered a lot of ground in this guide to heavy lifting! From understanding the concept of heavy lifting and its benefits to the fundamental principles of proper technique, progressive overload, and recovery to the essential exercises and safety tips, you’re now equipped with the knowledge to begin your heavy lifting journey.
Remember, heavy lifting isn’t just about the weights; it’s about proper technique, listening to your body, and fueling it right. So, are you ready to lift heavy and maximize your gains?
Frequently Asked Questions
Is heavy lifting good for you?
How many pounds is considered heavy lifting?
What are the key principles for effective heavy lifting?
Author
Sydney E.
-
Latest Posts
-
-
The Truth About Metabolism: What You Need to Know
-
Satiety: How to Feel Full and Satisfied
-
Functional Foods for Optimal Health: A Beginner’s Guide
-
Plyometrics for Beginners to Build Strength and Speed
-
Polyphasic Sleep Schedules: Benefits, Risks, and Practical Tips
-
-
Contacts
Contacts
967 E. Parkcenter Blvd #345
Boise, ID 83706
7 A.M. - 3 P.M. MST, Mon - Fri
(833) 332-8655
support@clinicaleffects.com
THE STATEMENTS MADE ON OUR WEBSITES HAVE NOT BEEN EVALUATED BY THE FDA (U.S. FOOD & DRUG ADMINISTRATION). OUR PRODUCTS ARE NOT INTENDED TO DIAGNOSE, CURE OR PREVENT ANY DISEASE. CLINICAL EFFECTS IS NOT AFFILIATED WITH ANY OF THE STUDIES MENTIONED ON THE WEBSITE. THE TESTIMONIALS ON THIS WEBSITE ARE INDIVIDUAL CASES AND DO NOT GUARANTEE THAT YOU WILL GET THE SAME RESULTS.
© All Rights Reserved 2021


